
With the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic, people’s expectation for economy to go back to the normal track has become increasingly urgent. Recently, a new phenomenon has caught the eyes of many scholars, that is, a“K-shaped recovery” of the U.S. economy. What is a“K-shaped recovery”? What are the factors at work behind such type of recovery? What changes will it bring to our daily life and work? What should we do to respond?
What is a“K-shaped recovery”?
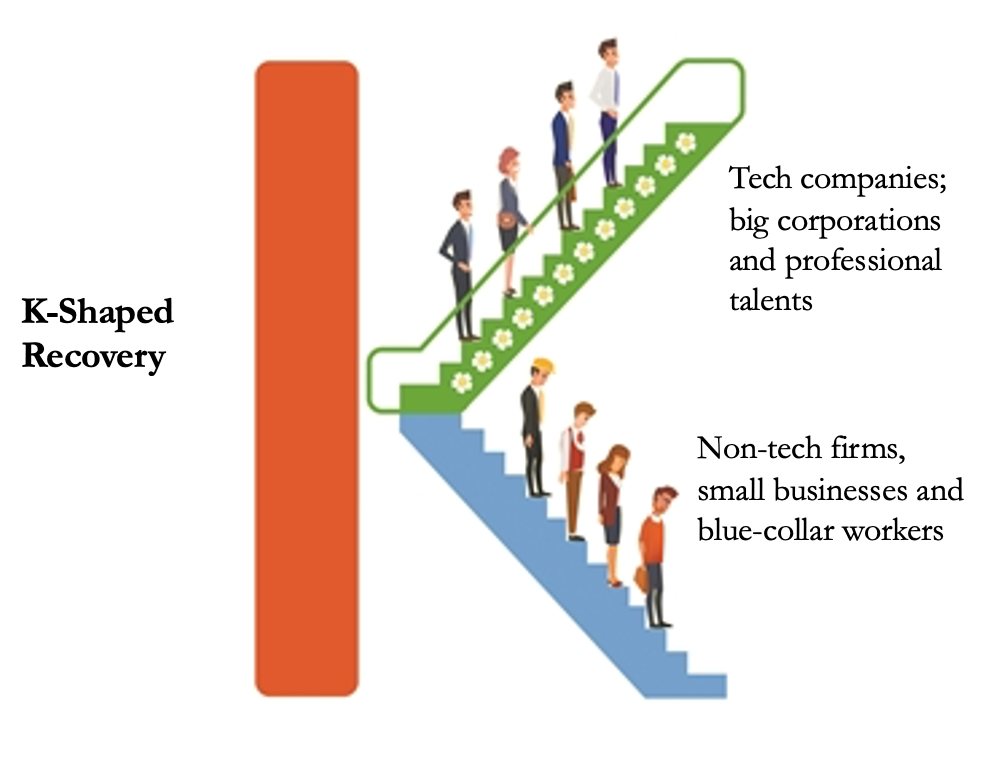
It is a common knowledge that the U.S. economy fell into a recession shortly after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. As a response, the U.S. government has launched rounds of economic stimulus with a relatively strong intensity, among which, quantitative easing (QE) is the most eye-catching one. Thanks to these stimulus packages, the U.S. economy begun to bounce back from the third quarter of 2020. According to the statistics, its economy increased by 33.4 percent in the third quarter compared with that of the previous one, and registered a 4 percent growth in the fourth quarter, which shows a slowing economic decline. However, instead of a“V-shaped” or“U-shaped” recovery characterized by a quick rebound after the economy hit the low point in previous crises, the U.S. economy is experiencing a“K-shaped” one. (See the diagram in the upper right). The two arms of the Roman letter“K” indicate the degree and the status of recovery. Specifically, the upper arm represents the tech companies, big corporations and virtual economy that enjoy a fast rebound and their working personnel, while the lower arm represents the non-tech firms and small businesses that struggle in a bleak recovery and their blue-collar workers. In this sense, the most striking feature exhibited by the“K-shaped recovery” is a divergent performance in economic recovery, which indicates an evidently uneven rebound across different regions, industries, sectors, businesses and groups of people in the economy.
Although the term“K-shaped recovery” is first used as a descriptor of the economic recovery in the U.S., the complicated divergence as its essential feature is an universal phenomenon across the globe. First, developed countries have bounced back ahead of their developing counterparts and other emerging countries and regions except for China. Second, the global financial sector recovers at a faster pace than the real economy. Third, the global hi-tech sector climbs back upward at a faster speed than other sectors. Fourth, knowledge-oriented and technical personnel are the first group of people to find jobs and achieve higher incomes during the pandemic, while the other types of personnel still suffer.
In 2020, China became the only big economy in the world that achieved positive economic growth. However, some signs of the“K-shaped recovery” can still be detected. From a regional perspective, regions and cities with an advanced high-tech industry, such as Hangzhou in the coastal area, register a relatively better economic performance and enjoy a more promising economic outlook than other regions and cities. From an industrial perspective, the financial sector, platform economy, and high-tech industry outperform the other industries and sectors to a significant extent in growth, especially the tourism and aviation industry that have been severely battered by the pandemic.
Objectively speaking, the“K-shaped recovery” is a double-edged sword to the world. It can be seen through two lens. In terms of its negative impacts, as an enormous amount of traditional enterprises remain mired in a sluggish recovery, the“K-shaped recovery” not only undermines the vigor of a huge amount of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) for surviving and thriving, but also disrupts the supply of daily necessities and services for civilians and sends ordinary individuals into unemployment, thus widening the gap between the haves and the have-nots and intensifying social contradictions. In the era of globalization, the impacts imposed by the transmission of external risks have risen to prominence. Meanwhile, as most of the countries turn to relatively loose fiscal and monetary policies in a bid to fight against the pandemic-induced depression, the“K-shaped recovery” may fuel the overheating of the virtual economy and truly impede the development of the real economy. In terms of its positive impacts, the“K-shaped recovery” optimizes the allocation of recourses to a certain degree. It directs capitals, technologies, talents and other important recourses to aggregate in the hi-tech and emerging industries, eliminate a batch of industries and production capacity that are backward in technologies and underperformed in environmental protection, and therefore expedite industrial transformation and upgrading.
Factors driving the“K-shaped recovery”
In order to understand the factors at work behind the“K-shaped recovery”, we first need to grasp the general essential feature of economic crisis. Marx’s theory of economic crisis reveals that economic crisis is also a process of industrial structure readjustment. After the outbreak of an economic crisis, enterprises with abundant capital and leading technology will take the crisis as an opportunity for capital expansion and technology upgrading. These large corporations become the first to get out of the mire of crisis through corporate merge and acquisition, equipment renewal, technological transformation and other means, while those companies with scarce capital, backward technologies and products of inaccurate market positioning get eliminated. In this sense, the divergence as an essential feature of the“K-shaped recovery” can be found to some extent in any kind of recoveries after an economic crisis.
The fact that such“K-shaped” divergence has emerged as an evident trend of global economic recovery and has become an universal phenomenon across the world is closely related to the current global economic and social reform, technological disruption and the impacts of the pandemic. The first factor is the acceleration of technological revolution. The new generation of information technology represented by digital technology as well as biotechnology represented by genetic engineering, in particular, are facilitating economic and social reform and development. Against such backdrop, countries, regions and enterprises in the leading position of the current technological revolution have inevitably shown strong resilience in the current economic crisis and have led recovery in post-crisis period. The second factor is globalization and application of internet. These two trends have given birth to a huge amount of transnational companies and internet platform operators which boast a strong capability in resisting risks and integrating resources. The third factor is macro-regulation. Faced with the disruption of industrial chains and supply chains caused by the unexpected attack of the pandemic as well as the consequent economic shutdown, countries and regions have adopted a series of macro-regulatory measures including proactive fiscal and monetary policies and industrial support policies. During the crisis, countries and regions with a powerful national strength have shown strong capability in regulation and therefore have widened the gap with other countries in economic recovery. However, it should be noted that after countries like the United States launched the QE, a large amount of stimulus funds flowed into the virtual economy such as the stock market while the real economy still stagnated in recession. As a result, an uneven recovery pattern in which the virtual economy bounces back far ahead of the real economy has formed. If the QE continues to be implemented in the United States, the inflation caused by it will inevitably ripple to the rest of the world; if the United States switches back to a tight monetary policy again, a reflux of capital will inevitably occur, which will give a heavy blow to the global stock market. Both aforementioned situations will bring greater challenges and difficulties to developing countries as they strive for economic recovery.
Insights from the“K-shaped recovery”
The occurrence of the“K-shaped recovery” is not only a result of the outbreak of the pandemic, but also an embodiment of the general essential feature of economic crisis; It is not only subject to the macro-regulation of government but also related to the current technological revolution. In the context of globalization and application of internet, the“K-shaped recovery” will inevitably generate a global influence. It will play out in the economic and social life of China to some extent, exerting an influence on the production and operation of Chinese enterprises, the employment and daily life of the Chinese people and the macro-regulatory policies of the Chinese government. Therefore, it needs our careful study and response.
For producers and corporate operators, the following strategies should be adopted to respond the“K-shaped recovery”: First, they should prioritize the performance and quality improvement of their products so as to enhance the market competitiveness of products. They should attach great importance to scientific and technological innovation and deploy advanced equipment, technologies and processes as much as possible to produce and provide products and services with a strong market competitiveness. Enterprises with favorable conditions, whether in emerging industries or traditional ones, should speed up their digital transformation. Second, the concept of achieving development through coordination and mutual-support should be established. The“K-shaped recovery” has also demonstrated that big corporations and the enterprises with a relatively complete industrial chain and supply chain have strong resilience against depression. Large corporations should follow the concept of achieving coordinated development and innovation in industrial chains and supply chains to form a community with the SMEs. SMEs should proactively integrate themselves into the industrial chains led by the market-dominant products of large companies. Third, enterprises and their operators should have a strong sense of social responsibility. In the modern market economy, social responsibility has become a necessary prerequisite for the corporate survival and flourishment. Companies without a sense of social responsibility, together with their products, will be rejected by the society and will not be accepted and supported by consumers. Therefore, when responding the pandemic-induced economic downturn, enterprises should surmount challenges, treat employees well, and work hard in such aspects as arranging positions for employees and maintaining their wage level. Only in this way, can employees be loyal to their enterprises and work with their enterprises in solidarity to get over difficulties. Fourth, the enterprises in the real economy should buttress the bottom line of developing the real economy, not being allured by the temporary bubble boom of the virtual economy which may cause a huge damage. Enormous cases have proved that overspeculation in the virtual economy will undermine the fundamentals of enterprises for development in the end.
For employees, the following measures should be taken to adapt to economic downturn and to keep up with the“K-shaped recovery”: First, they should be mentally prepared for a new job or a new position. Due to the pandemic, some industries have been heavily hit, including tourism, film, training, MICE (Meeting, Incentive, Conference, Exhibition) and relevant product manufacturing. The number of workforce in these industries has been slashed. Additionally, the acceleration of technological innovation has sped up the replacement of old sectors with new ones, a phenomenon making job positions unstable. Employees should face up to this situation positively and take the change of job and position as a normal. Second, they should accelerate the update of their knowledge and skills. Behind the“K-shaped recovery” are factors like knowledge and skill at work and lies a contest between advanced industrial technologies and backward ones. Therefore, employees should pursue continuing learning and retraining so that their knowledge structure and skills can keep up with the pace of industrial development.
For the government, it should face up to the“K-shaped recovery” and take appropriate regulatory measures to hold the bottom line of ensuring people’s wellbeing on the one hand, and to promote the industrial transformation and upgrading on the other by guiding the situation to develop towards a favorable direction and riding favorable momentum. First, the government should vigorously support the development of micro, small, medium-sized enterprises which focus on technological breakthroughs and people’s wellbeing, and help enterprises, especially those on their growth stage, actively adapt to the rapid development of the digital economy. For Guangzhou, efforts must be made to forge the brand of“Made in Guangzhou” and“Guangzhou Service”, and expand the domestic and overseas market share of local goods and services. Second, key industries should be supported in forming local industrial chains in key links so that the coordinated innovation and development among local enterprises can be realized. Enterprises committed to the research and development of key technologies as well as the manufacturing of key components should be retained in China, and should be supported in collaborating with their overseas counterparts to form a mutually supported enterprise system, which is also one of the secrets enabling some big enterprises to gain the upper hand in the current“K-shaped recovery”.